-
1 asynchrones Drehmoment
Deutsch-Englisch Wörterbuch der Elektrotechnik und Elektronik > asynchrones Drehmoment
-
2 электродвигатель
electric motor
(рис. 90)
- азимутальной коррекции (гироагрегата гик) — azimuth torque motor
-, асинхронный — asynchronous motor
-, гистерезисный — hysteresis motor
синхронный эл. дв. без выступающих полюсов н возбуждения пост. током. — a synchronous motor without salient poles or direct-current excitation.
- горизонтальной коррекции (эдгк) — leveling torque motor
-, индукционный — induction motor
эл. двиг. переменного тока, у которого основная (статорная) обмотка соединяется с источником питания и взаимодействует с обмоткой ротора (обычно типа "беличье колесо") — an alternating-current motor in which the primary winding (usually the stator) is connected to the power source and induces а current into a polyphase secondary or squirred-cage secondary winding (usually the rotor).
-, исполнительный — servomotor, servo electric motor
эл. двиг. в системе сервоуправлания. обороты двигателя регулируются коррекционным эл. сигналом, усиливаемым и подаваемым в цепь электродвигателя. — а motor used in а servo system. its rotation or speed (or both) are controlled by a corrective electric signal that has been amplified and fed into the motor circuit.
-, компаундный — compound-wound motor
эл. двиг. постоянного тока с двумя отдельными обмотками возбуждения. одна обмотка включена параллельно, a другая последовательно обмотке якоря. — а d-c motor having two separate field windings. one, usually the predominant field, is connected in parallel with the armature circuit and the other is connected in series.
-, коррекционный (гироскопа) — erection torque motor /torquer/
-, сериесный — series motor
эл. двиг. с обмоткой возбуждения, включенной последовательно с обмоткой якоря. — а motor in which the field and armature circuits are connected in series.
-, синхронный — synchronous motor
an induction motor which runs at synchronous speed.
- следящей системы — servomotor
- следящей системы (рамки гироплатформы) — gimbal servomotor
-, шумовой — shunt-wound motor
эл. двиг. постоянного тока с обмоткой возбуждения, включенной параллельно обмотке якоря. — а direct-current motor in which the field circuit and armature circuit are connected in parallel.Русско-английский сборник авиационно-технических терминов > электродвигатель
-
3 прямой пуск вращающегося электродвигателя
- full voltage starter application
- DOL
- direct-on-line starting
- direct starting
- direct operation of a motor
- direct line starting
- across-the-line starting (US)
прямой пуск вращающегося электродвигателя
Пуск вращающегося электродвигателя путем непосредственного подключения его к питающей сети.
[ ГОСТ 27471-87]EN
direct-on-line starting
across-the-line starting (US)
the process of starting a motor by connecting it directly to the supply at rated voltage
[IEV number 411-52-15]FR
démarrage direct
mode de démarrage d'un moteur, consistant à lui appliquer directement sa pleine tension assignée
[IEV number 411-52-15]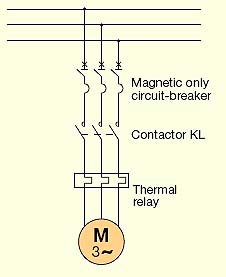
Рис. ABB
Схема прямого пуска электродвигателяMagnetic only circuit-breaker - Автоматический выключатель с электромагнитным расцепителем
Contactor KL - Контактор KL
Thermal relay - Тепловое реле
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
Direct-on-line starting
Direct-on-line starting, which is often abbreviated as DOL, is perhaps the most traditional system and consists in connecting the motor directly to the supply network, thus carrying out starting at full voltage.Direct-on-line starting represents the simplest and the most economical system to start a squirrel-cage asynchronous motor and it is the most used.
As represented in Figure 5, it provides the direct connection to the supply network and therefore starting is carried out at full voltage and with constant frequency, developing a high starting torque with very reduced acceleration times.
The typical applications are relevant to small power motors also with full load starting.
These advantages are linked to some problems such as, for example, the high inrush current, which - in the first instants - can reach values of about 10 to 12 times the rated current, then can decrease to about 6 to 8 times the rated current and can persist to reach the maximum torque speed.The effects of such currents can be identified with the high electro-dynamical stresses on the motor connection cables and could affect also the windings of the motor itself; besides, the high inrush torques can cause violent accelerations which stress the transmission components (belts and joints) generating distribution problems with a reduction in the mechanical life of these elements.
Finally, also the possible electrical problems due to voltage drops on the supply line of the motor or of the connected equipment must be taken into consideration.
[ABB]Прямой пуск
Прямой пуск, который по-английски часто сокращенно обозначают как DOL, является, пожалуй наиболее распространенным способом пуска. Он заключается в непосредственном (т. е. прямом) подключении двигателя к питающей сети. Это означает, что пуск двигателя осуществляется при полном напряжении.Схема прямого пуска является наиболее простым, экономичным и чаще всего применяемым решением для электродвигателей с короткозамкнутым ротором.
Схема прямого подключения к сети представлена на рисунке 5. Пуск осуществляется при полном напряжении и постоянной частоте сети. Электродвигатель развивает высокий пусковой момент при коротком времени разгона.
Типичные области применения – маломощные электродвигатели, в том числе с пуском при полной нагрузке.
Однако, наряду с преимуществами имеются и определенные недостатки, например, бросок пускового тока, достигающий в первоначальный момент 10…12-кратного значения от номинального тока электродвигателя. Затем ток двигателя уменьшается примерно до 6…8-кратного значения номинального тока и будет держаться на этом уровне до тех пор, пока скорость двигателя не достигнет максимального значения.
Такое изменение тока оказывает значительное электродинамическое воздействие на кабель, подключенный к двигателю. Кроме того пусковой ток воздействует на обмотки двигателя. Высокий начальный пусковой момент может привести к значительному ускорению и следовательно к значительной нагрузке элементов привода (ремней, крепления узлов), что вызывает сокращение их срока службы.
И, наконец, следует принять во внимание возможное возникновение проблем, связанных с падением напряжения в линии питания двигателя и подключенного к этой линии оборудования.
[Перевод Интент]
Тематики
Синонимы
EN
- across-the-line starting (US)
- direct line starting
- direct operation of a motor
- direct starting
- direct-on-line starting
- DOL
- full voltage starter application
DE
FR
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > прямой пуск вращающегося электродвигателя
-
4 электродвигатель
electromotor, electric motor, motor* * *электродви́гатель м.
(electric) motorвключа́ть электродви́гатель — start [switch on, turn on, energize] a motorзащища́ть электродви́гатель — protect a motorзащища́ть электродви́гатель пла́вким предохрани́телем — fuse a motorиспо́льзовать электродви́гатель с недогру́зкой — run a motor lightэлектродви́гатель облада́ет сво́йствами обрати́мости — a motor can operate as a generatorотключа́ть [выключа́ть] электродви́гатель — stop [de-energize, switch off, turn off] a motorохлажда́ть электродви́гатель принуди́тельно — force-cool a motorэлектродви́гатель развива́ет (такой-то [m2]) враща́ющий моме́нт — an electric motor develops a torque of … (kgm)сжечь электродви́гатель — burn a motorста́вить электродви́гатель под нагру́зку — put load on a motor; load a motorуправля́ть электродви́гателем — control a motorасинхро́нный электродви́гатель — induction [asynchronous] motorасинхро́нный, синхронизи́рованный электродви́гатель — synchronous induction motorасинхро́нный электродви́гатель с короткоза́мкнутым ро́тором — squirrel-cage induction motorасинхро́нный электродви́гатель с фа́зным ро́тором — брит. slip-ring induction motor; амер. phase-wound(-rotor) motorбесколле́кторный электродви́гатель — commutatorless [brushless] motorбесщё́точный электродви́гатель — brushless motorбрызгозащищё́нный электродви́гатель — splash proof motorвентили́руемый электродви́гатель — ventilated motorве́нтильный электродви́гатель — thyratron motorвзрывозащищё́нный электродви́гатель — explosion-proof [flame-proof] motorвстра́иваемый электродви́гатель — built-in motorгазонепроница́емый электродви́гатель — gas-tight motorгистере́зисный электродви́гатель — hysteresis motorгребно́й электродви́гатель — main propulsion motorгребно́й электродви́гатель авари́йного хо́да мор. — emergency propulsion motorдвухпо́люсный электродви́гатель — bipolar motorзакры́тый электродви́гатель — totally enclosed motorколле́кторный электродви́гатель — commutator motorконденса́торный электродви́гатель — capacitor-start motorкороткоза́мкнутый электродви́гатель — squirrel cage motorмногофа́зный электродви́гатель — polyphase motorнереверси́вный электродви́гатель — non-reversible motorнеявнопо́люсный электродви́гатель — nonsalient-pole [round rotor] motorоднофа́зный электродви́гатель — single-phase motorэлектродви́гатель переме́нного то́ка — alternating current [a.c.] motorпогружно́й электродви́гатель — submersible motorэлектродви́гатель постоя́нного то́ка — direct-current [d.c.] motorпусково́й электродви́гатель — starting motorреакти́вный электродви́гатель — reaction motorреду́кторный электродви́гатель — gearmotorрепульсио́нный электродви́гатель — repulsion induction motorэлектродви́гатель с бе́личьей кле́ткой — squirrel-cage motorэлектродви́гатель с двойно́й бе́личьей кле́ткой — double squirrel-cage motorсе́риесный электродви́гатель — series(-wound) motorэлектродви́гатель с жё́сткой характери́стикой — constant-voltage [flat-response] motorсинхро́нный электродви́гатель — synchronous motorэлектродви́гатель с конта́ктными ко́льцами — slip-ring motorследя́щий электродви́гатель — servo motorэлектродви́гатель с мя́гкой характери́стикой — drooping-response motorэлектродви́гатель с печа́тной обмо́ткой — printed circuit motorэлектродви́гатель с после́довательным возбужде́нием — series(-wound) motorэлектродви́гатель с принуди́тельным возду́шным охлажде́нием — forced-air-cooled motorэлектродви́гатель с регули́руемой ско́ростью враще́ния — adjustable [variable] speed motorэлектродви́гатель с самовентиля́цией — self-ventilated motorэлектродви́гатель с сегме́нтным ро́тором — segmental-rotor motorэлектродви́гатель с фа́зным ро́тором — phase-wound (rotor) motorтя́говый электродви́гатель — traction motorуниверса́льный электродви́гатель — universal motorфла́нцевый электродви́гатель — flange(-mounted) motorша́говый электродви́гатель — step(ping) motorшунтово́й электродви́гатель — shunt(-wound) motorщитово́й электродви́гатель — endshield-mounted motorявнопо́люсный электродви́гатель — salient-pole motorРусско-английский политехнический словарь > электродвигатель
См. также в других словарях:
Direct torque control — (DTC) is one method used in variable frequency drives to control the torque (and thus finally the speed) of three phase AC electric motors. This involves calculating an estimate of the motor s magnetic flux and torque based on the measured… … Wikipedia
Electric motor — For other kinds of motors, see motor (disambiguation). For a railroad electric engine, see electric locomotive. Various electric motors. A 9 volt PP3 transistor battery is in the center foreground for size comparison. An electric motor converts… … Wikipedia
Singly-fed electric machine — Singly fed electric machines (i.e., electric motors or electric generators) belong to a category of electric machines that incorporate one multiphase winding set, which is independently excited, actively participates in the energy conversion… … Wikipedia
Doubly fed electric machine — Doubly fed electric machines are electric motors or electric generators that have windings on both stationary and rotating parts, where both windings transfer significant power between shaft and electrical system. Doubly fed machines are useful… … Wikipedia
Motor controller — A motor controller is a device or group of devices that serves to govern in some predetermined manner the performance of an electric motor.[1] A motor controller might include a manual or automatic means for starting and stopping the motor,… … Wikipedia
Electric actuator — Actuators are used for the automation of industrial valves and can be found in all kinds of technical process plants: they are used in wastewater treatment plants, power plants and even refineries. This is where they play a major part in… … Wikipedia
Motor soft starter — Examples of motor soft starters [1] A motor soft starter is a device used with AC electric motors to temporarily reduce the load and torque in the powertrain of the motor during startup. This reduces the mechanical stress on the motor and shaft,… … Wikipedia
Brushless DC electric motor — A microprocessor controlled BLDC motor powering a micro remote controlled airplane. This external rotor motor weighs 5 grams, consumes approximately 11 watts (15 millihorsepower) and produces thrust of more than twice the weight of the plane … Wikipedia
AC motor — An AC motor is an electric motor that is driven by an alternating current. It consists of two basic parts, an outside stationary stator having coils supplied with AC current to produce a rotating magnetic field, and an inside rotor attached to… … Wikipedia
Variable frequency transformer — A variable frequency transformer is used to transmit electricity between two asynchronous alternating current domains. The VFT is a relatively recent development (first deployed in 2004). Most grid interties use high voltage direct current… … Wikipedia
Wind turbine design — An example of a wind turbine, this 3 bladed turbine is the classic design of modern wind turbines Wind turbines History Design … Wikipedia
